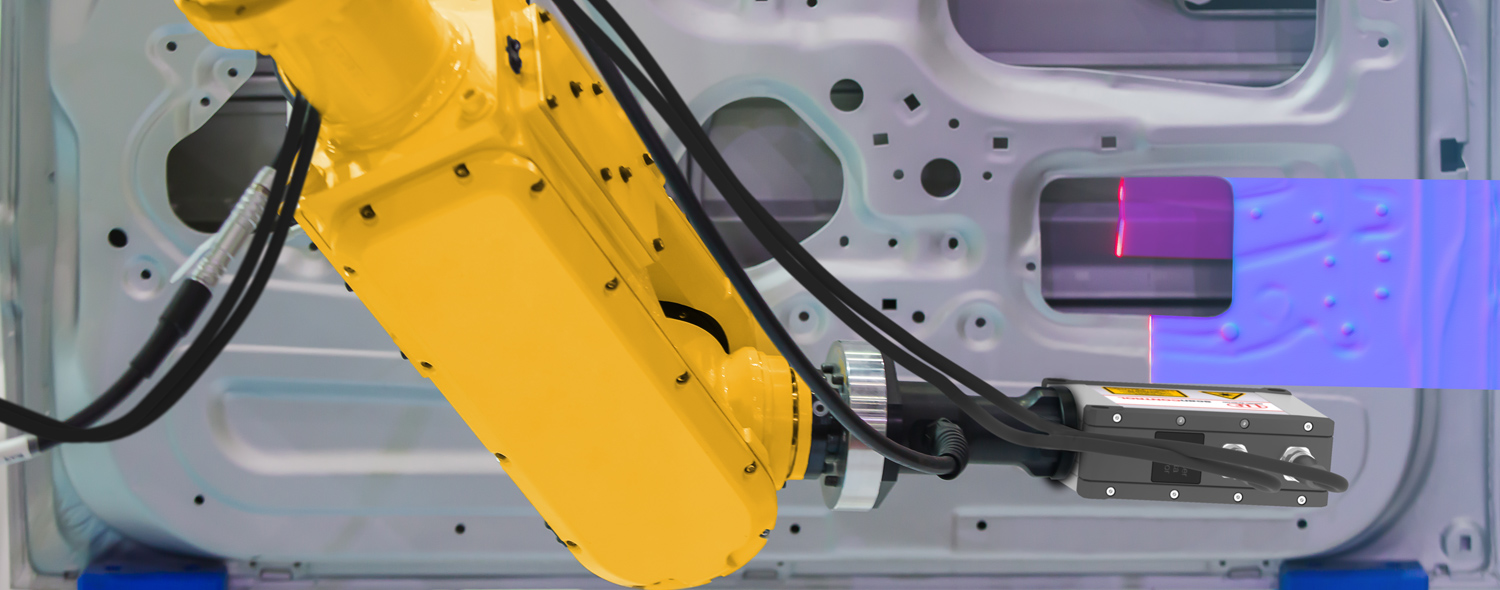
3D laser scanners for automation and quality assurance
3D laser scanners play a crucial role in modern image processing by setting new standards in the acquisition of three-dimensional data. 3D scanners from Micro-Epsilon precisely capture entire objects and surfaces, outperforming conventional sensor technologies. Industries such as robotics, automation, quality control and logistics benefit considerably from innovative 3D measurement technology.
What are 3D laser scanners and how do they work?
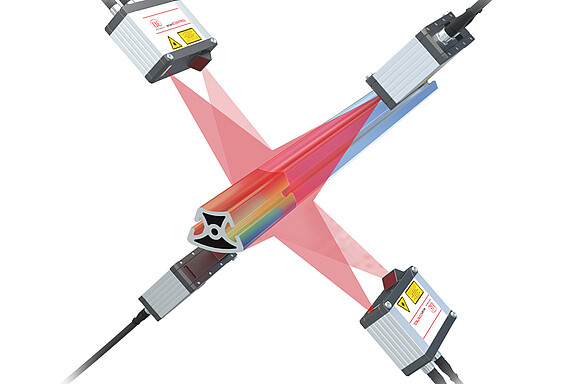
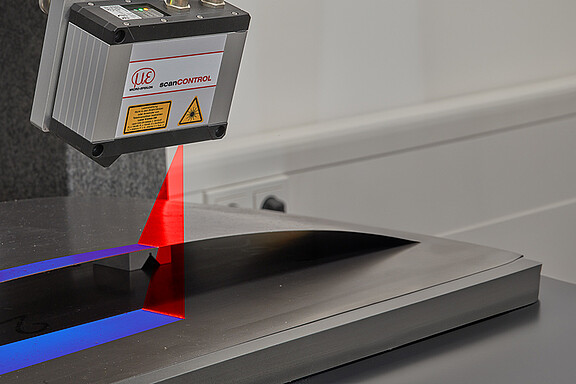
A 3D laser scanner projects a laser line onto the object to be measured. The reflected light is imaged on a matrix in the scanner and evaluated as a profile. If the object moves under the sensor or the scanner is moved over the object, a 3D point cloud is generated from the sequence of profiles.
This technology enables precise three-dimensional recognition of shapes, volumes and surface structures in real time. This method of non-contact data acquisition prevents mechanical wear, which makes these scanners particularly durable and efficient.
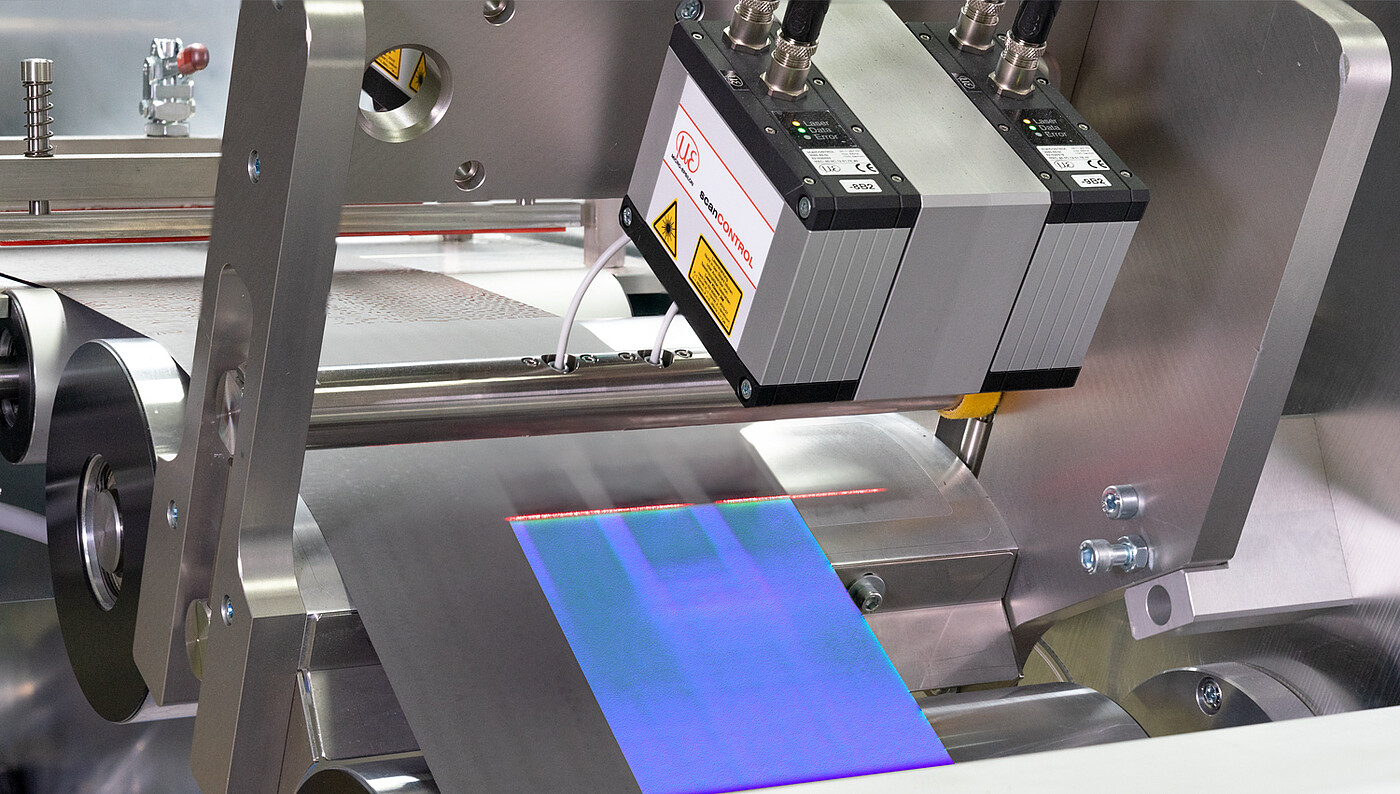


Advantages of 3D laser scanners
- Real-time 3D data: Perfect for dynamic applications with fast movements.
- High precision: Capture exact depth information and the finest of surface details.
- Flexibility: Versatile use on various materials and in different environments.
- Ease of integration: Compatible with modern image processing systems and easy to integrate into existing systems.
What are the advantages of 3D laser scanners for modern applications?
3D laser scanners are indispensable in precise and fast 3D measurements. Non-contact data acquisition enables their use in sensitive and demanding areas. In automation and robotics in particular, they ensure precise geometry measurements and efficient work processes.
Key advantages at a glance:
- Speed: High-precision 3D scans in real time.
- High-resolution detection: Detection of the finest of details in geometry measurements and surface analyses.
- Robustness: Use in dynamic environments and on a wide variety of materials.
- Low weight: for use on robots
- Red and blue laser: Measurement on numerous surfaces
FAQ
3D scanners from Micro-Epsilon are based on the triangulation principle. A laser line is projected onto the object to be measured. The reflected light is imaged and evaluated in the scanner. If the object moves under the sensor or the scanner is moved over the object, a 3D point cloud is generated from the sequence of individual scans. The 3D laser scanners are available with different measuring ranges. Depending on the measurement task, a scanner with blue laser light or red laser light can be used
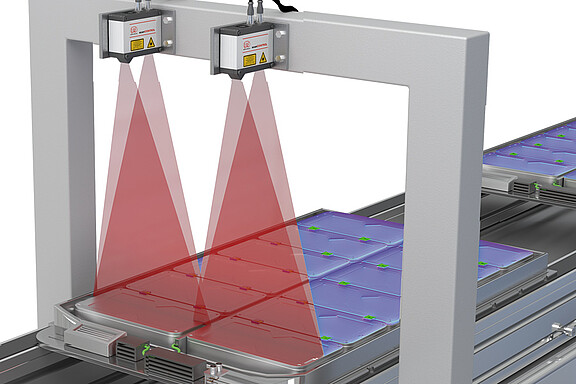
3D scanners are used in numerous industries and fields of application.
They can be used on the rotary indexing table, on the robot or integrated into a machine. Attached to a conveyor belt, these 3D scanners inspect the 3D geometry of products. They typically measure geometry, presence, texture, position and surface.
Depending on the sensor type, various measuring ranges are available.
3D laser scanners evaluate individual profiles. Consecutively arranged, these profiles form the 3D point cloud. 3D sensors such as the 3D snapshot sensors from Micro-Epsilon generate one 3D point cloud per image.
The accuracy of a 3D scanner is determined by several factors, including the scanning technology, the surface quality of the object, the resolution of the scanner and the ambient conditions such as light and temperature. Sophisticated industrial 3D scanners achieve accuracies in the micrometer range.
Rely on precision and efficiency: 3D scanning for your industry
Our 3D scanners are specially designed for fast and precise 3D scans. Optimally adapted to various fields of application, they ensure maximum efficiency in production and automation.
Get in touch with us for more information and individual advice on integrating 3D laser scanners into your systems!